Are you looking for effective tax planning strategies to keep more of your hard-earned income? This article provides essential tax tips to help you maximize your deductions, minimize your tax liability, and ultimately, retain a greater portion of your earnings. Learn how smart tax planning can significantly impact your financial well-being and help you achieve your financial goals.
Understanding How Income Tax Works
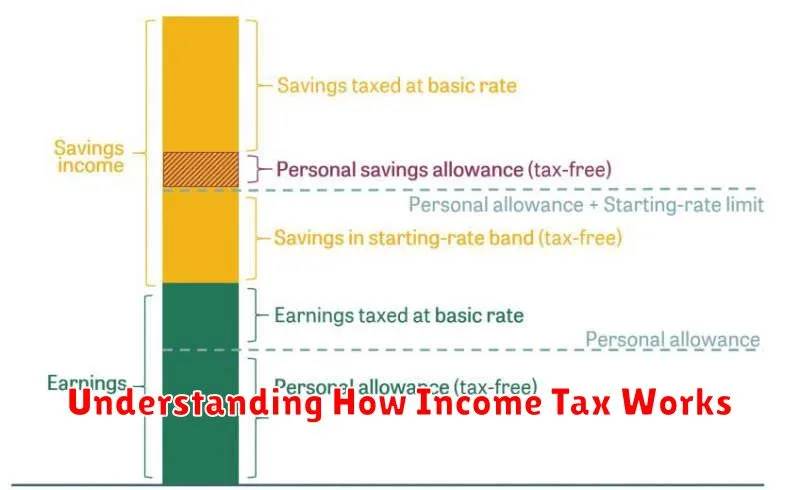
Understanding how income tax works is crucial for effective tax planning. Income tax is a tax levied on your earnings, whether from employment, self-employment, investments, or other sources. The amount you owe depends on your taxable income, which is your gross income minus certain deductions and adjustments.
The taxable income is then used to determine your tax bracket. Tax brackets are ranges of income subject to specific tax rates. A progressive tax system, like that in many countries, means higher earners pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes. It’s important to note that you don’t pay the highest rate on your entire income; you only pay the higher rate on the portion of your income that falls within that specific bracket.
Several factors influence your tax liability, including your filing status (single, married filing jointly, etc.), number of dependents, and available tax deductions and tax credits. Deductions reduce your taxable income, while credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Understanding these factors is key to minimizing your tax burden.
Accurate record-keeping is paramount. Maintain detailed records of all income and expenses relevant to your tax situation. This will allow for accurate calculation of your taxable income and will assist in identifying opportunities to reduce your tax liability through legitimate means.
Using Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Tax-advantaged accounts offer significant benefits for reducing your overall tax burden. These accounts allow you to either deduct contributions from your taxable income (like a traditional IRA or 401(k)) or let your investment earnings grow tax-deferred (like a Roth IRA or 401(k)).
Retirement accounts such as 401(k)s and IRAs are popular choices. Contributions to traditional versions may be tax-deductible, reducing your current year’s taxable income. Roth versions offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement after a specified period, which can save you significantly on taxes later. The best option depends on your current tax bracket and projected future tax bracket.
Health savings accounts (HSAs) are another excellent option, particularly if you have a high-deductible health plan. Contributions are tax-deductible, grow tax-free, and can be withdrawn tax-free for qualified medical expenses. This provides a triple tax advantage.
529 plans are designed for education savings. Contributions may not be tax-deductible at the federal level but may offer state-level tax benefits. Earnings grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals are tax-free when used for qualified education expenses. Each state’s rules may vary.
Careful planning is crucial when choosing and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts. Consulting with a financial advisor can help determine which accounts best align with your individual financial goals and tax situation.
Deductions and Credits You Might Be Missing
Many taxpayers overlook valuable deductions and credits that can significantly reduce their tax liability. Careful tax planning is crucial to identifying and claiming these.
One often-missed deduction is for self-employment taxes. If you’re self-employed, you can deduct one-half of your self-employment tax payments. Similarly, home office deductions are frequently underutilized. If you use a portion of your home exclusively and regularly for business, you may be able to deduct expenses related to that space.
Several valuable credits may also be overlooked. The Child Tax Credit, for example, can provide substantial relief for families with qualifying children. The American Opportunity Tax Credit and Lifetime Learning Credit can help offset the cost of higher education. Additionally, credits are available for certain healthcare expenses and for energy-efficient home improvements. Eligibility requirements vary, so it’s vital to review the current IRS guidelines.
To ensure you don’t miss out, thoroughly review your personal finances and consult the IRS publications or a qualified tax professional. Taking the time to investigate these potential deductions and credits can lead to considerable tax savings.
How to Organize Finances for Tax Season
Effective tax planning starts with organized finances. Begin by gathering all relevant financial documents. This includes W-2s, 1099s, receipts for deductible expenses (charitable donations, medical expenses, etc.), and bank statements.
Categorize your documents. Create separate folders or files for each category to streamline the process. Using a spreadsheet or tax software can further simplify organization and help you track deductions and credits effectively.
Keep accurate records throughout the year. This proactive approach minimizes stress during tax season and allows for more accurate tax preparation. Consider using a cloud-based storage system for easy access and backup of your important financial documents.
Review your previous year’s tax return. This provides a baseline for comparison and helps identify areas where you might improve your organization for the current year. Understanding your past tax situation is crucial for informed future tax planning.
Keeping Track of Expenses All Year
Maintaining accurate records of your expenses throughout the year is crucial for effective tax planning. This allows you to maximize deductions and minimize your tax liability.
Consider using a dedicated expense tracking system, whether it’s a spreadsheet, budgeting app, or even a simple notebook. Be sure to record all relevant information, including the date, description, and amount of each expense. Categorize expenses to easily identify those that are tax-deductible.
Organize receipts and other supporting documentation. Keep them well-organized and readily accessible for tax preparation. Digital organization is efficient, but ensure you have backups to prevent data loss. Proper record-keeping facilitates a smoother and more accurate tax filing process.
Tracking expenses allows you to identify areas where you may be able to reduce spending in the future and to more accurately plan your tax strategy for the upcoming year. This proactive approach ultimately helps you retain more of your hard-earned income.
When to Work with a Tax Professional

While many individuals can handle their taxes independently, consulting a tax professional is crucial in certain situations. Their expertise can save you money and prevent costly mistakes.
Consider seeking professional help if you have a complex tax situation, such as owning a business, investing in real estate, or having significant capital gains. Self-employment income also frequently requires specialized tax knowledge.
If you’re facing a tax audit or anticipate potential tax issues, engaging a tax professional is highly recommended. They can represent you and help navigate the process effectively.
Furthermore, if you’re unsure about the best tax strategies for your unique circumstances, a tax professional can provide valuable guidance and planning, helping you minimize your tax liability and maximize your after-tax income.
Ultimately, the decision of when to engage a tax professional depends on your individual needs and comfort level. However, seeking expert advice can be a wise investment, particularly in complex situations.
Tax Planning for Freelancers and Side Hustlers
Freelancers and side hustlers face unique tax challenges. Unlike traditional employees, they’re responsible for paying both self-employment and income taxes, often quarterly. Careful planning is crucial to minimize your tax burden and maximize your income retention.
Accurate record-keeping is paramount. Maintain detailed records of all income and expenses, including mileage, supplies, and home office deductions (if applicable). This meticulous record-keeping will support your tax filings and potentially reduce your taxable income.
Understanding deductions is essential. Freelancers can deduct a variety of business expenses, significantly impacting their overall tax liability. Explore deductions for self-employment tax, home office expenses, health insurance premiums, and professional development. Consulting a tax professional can help identify all applicable deductions.
Tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as SEP IRAs or solo 401(k)s, offer significant tax benefits. Contributions are often tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income, and earnings grow tax-deferred. This strategy helps lower your current tax liability while building retirement savings.
Planning for estimated taxes is critical. Freelancers are responsible for paying estimated taxes quarterly. Underestimating these payments can result in penalties. Accurate projections of income and expenses are vital to avoid penalties and maintain financial stability.
Regularly review your financial situation and tax strategies. Tax laws and your personal financial circumstances change over time, necessitating regular assessment and adjustments to your tax planning approach. Seeking professional tax advice is a wise investment.
Avoiding Common Tax Mistakes
Careful tax planning can significantly increase your net income. One crucial aspect is avoiding common mistakes that lead to unnecessary tax burdens. Understanding these pitfalls is the first step towards maximizing your returns.
A frequent error is underestimating your tax liability. Accurately tracking income and deductions throughout the year is essential. Utilizing tax software or consulting a professional can significantly aid in accurate estimations.
Many taxpayers overlook available tax deductions and credits. Researching eligible deductions, such as charitable contributions or home office expenses, can substantially reduce your taxable income. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure you don’t miss any opportunities.
Failing to file on time is another common mistake with significant consequences, including penalties and interest. Mark your tax filing deadline well in advance and plan accordingly to avoid late filing penalties.
Finally, inaccurate record-keeping can lead to audits and complications. Maintain organized records of all income and expenses. Digital record-keeping is increasingly popular and can simplify this process while ensuring better data security.
By diligently addressing these areas, taxpayers can significantly improve their tax efficiency and retain a greater portion of their hard-earned income.

