Navigating the world of insurance can be daunting, with a plethora of policies available. This article will help you understand which insurance policies you truly need to protect yourself and your assets. We’ll demystify the complexities of insurance coverage, enabling you to make informed decisions about your financial protection and avoid unnecessary expenses. Learn how to assess your individual risk tolerance and choose the best insurance plans to suit your specific circumstances.
The Role of Insurance in Financial Protection
Insurance plays a crucial role in financial protection by mitigating the risk of significant financial losses due to unforeseen events. It acts as a safety net, offering a means of recovering from potentially devastating circumstances.
Various insurance policies address different types of risks. For example, health insurance protects against high medical expenses, while auto insurance covers accidents and liability. Homeowner’s or renter’s insurance safeguards against property damage or theft. Life insurance provides financial security for dependents in the event of the policyholder’s death.
The core function of insurance is risk transfer. By paying premiums, individuals transfer the financial burden of potential losses to the insurance company. In exchange, the insurer agrees to compensate the insured for covered losses, up to the policy limits.
Financial stability is a major benefit of insurance. Without it, individuals and families could face crippling debt from unexpected medical bills, property damage, or lawsuits. Insurance helps maintain financial stability, allowing individuals to focus on recovery rather than overwhelming financial distress.
Ultimately, insurance provides peace of mind. Knowing that financial protection is in place for various life events enables individuals to manage risks more effectively and make informed decisions about their future.
Types of Insurance Everyone Should Consider
Understanding insurance can feel overwhelming, but some policies offer crucial protection for everyone. Health insurance is paramount, covering medical expenses and promoting preventative care. The costs of even minor illnesses can be crippling without it.
Auto insurance is a legal requirement in most places, protecting you financially in the event of an accident. It covers damage to your vehicle and potential liability for injuries or damages to others.
Homeowners or renters insurance safeguards your belongings and provides liability protection. Homeowners insurance covers damage to your property, while renters insurance protects your personal possessions and offers liability coverage within your rental unit.
While not universally required, life insurance provides financial security for your dependents in the event of your death. It helps ensure your family’s financial stability after your passing.
Finally, consider disability insurance. This policy replaces a portion of your income if you become unable to work due to illness or injury, offering crucial financial support during a difficult time.
Health Insurance: Choosing the Right Plan
Choosing the right health insurance plan requires careful consideration of several key factors. First, understand your budget. Premiums, deductibles, and co-pays significantly impact your out-of-pocket costs. Compare plans within your price range.
Next, assess your healthcare needs. Consider your current health status, anticipated medical expenses, and the frequency of doctor visits. A plan with a lower premium but high deductible might be suitable if you are generally healthy, while a higher-premium plan with lower out-of-pocket costs might be preferable if you anticipate significant medical expenses.
Network providers are crucial. Check if your preferred doctors and specialists are included in the plan’s network. Using in-network providers generally results in lower costs. Review the plan’s formulary to ensure your prescription medications are covered.
Finally, understand the plan’s coverage details. Pay close attention to the deductible, co-pay, and out-of-pocket maximum. Compare different plans based on these factors to determine the best value for your specific needs and budget.
Life Insurance: Term vs Whole Explained
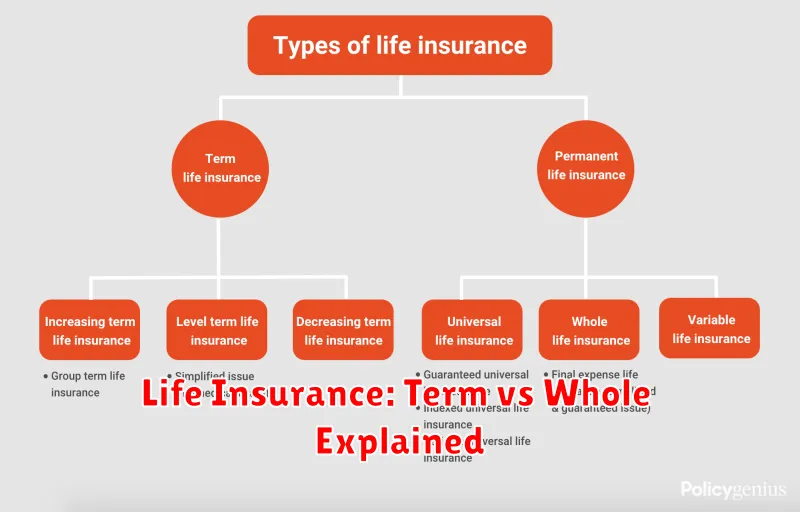
Choosing the right life insurance policy is crucial for securing your family’s financial future. Two main types dominate the market: term life insurance and whole life insurance. Understanding their key differences is essential for making an informed decision.
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, or “term,” such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If you die within the term, your beneficiaries receive a death benefit. Premiums are generally lower than whole life insurance, making it a more affordable option, particularly for younger individuals. However, coverage ends at the end of the term unless renewed, often at a significantly higher rate.
Whole life insurance, on the other hand, offers lifelong coverage. It builds a cash value component that grows tax-deferred over time. This cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, offering flexibility. However, premiums are considerably higher than term life insurance, and the death benefit may not be as substantial compared to the total premiums paid.
The best choice depends on your individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Consider factors like your age, financial stability, family responsibilities, and long-term financial objectives when deciding between term and whole life insurance.
Auto and Home Insurance Essentials
Auto insurance is crucial for protecting yourself financially in the event of an accident. Liability coverage is essential, paying for damages to others’ property or injuries sustained by others in an accident you cause. Collision and comprehensive coverage protect your own vehicle from damage, whether caused by an accident or other events. Consider factors like your vehicle’s value and your financial situation when choosing coverage levels.
Home insurance safeguards your most valuable asset – your home. It covers damage from various perils, including fire, theft, and weather events. Dwelling coverage protects the structure of your home, while personal property coverage covers your belongings inside. Liability coverage protects you financially if someone is injured on your property. Selecting adequate coverage ensures you’re protected against significant financial losses in the event of a disaster.
While other types of insurance exist, auto and home insurance are foundational for most individuals. Understanding the essential components of these policies ensures you have appropriate protection against unforeseen events and financial burdens.
Disability and Income Protection Coverage
Disability insurance protects your income if you become unable to work due to illness or injury. It replaces a portion of your earnings, allowing you to meet financial obligations while you recover. There are two main types: short-term and long-term. Short-term disability insurance typically covers a few months, while long-term disability insurance can provide coverage for years, even until retirement.
Income protection insurance, often overlapping with disability insurance, offers broader coverage, sometimes including protection against unemployment or other income disruptions. The specifics of coverage vary widely depending on the policy. It’s crucial to understand the definition of disability within the policy, the waiting period before benefits begin, and the benefit period (how long benefits are paid).
Consider the cost of the premiums versus the potential financial hardship of being unable to work. Your need for this coverage depends on factors like your profession, health status, and financial responsibilities. Consult with an insurance professional to determine the appropriate level of coverage for your individual circumstances.
How to Avoid Being Over- or Under-Insured
Finding the right insurance coverage requires a careful balance. Being underinsured leaves you vulnerable to significant financial losses in the event of an accident or disaster. Conversely, being overinsured means paying more than necessary for coverage you may never need.
To avoid underinsurance, accurately assess your assets and potential liabilities. Consider factors like the replacement cost of your home, the value of your possessions, and potential lawsuit costs. Work with an insurance professional to determine appropriate coverage levels for each type of insurance you carry.
Preventing overinsurance involves regularly reviewing your policies. As your circumstances change—you pay off a mortgage, reduce debt, or acquire less valuable possessions—your insurance needs may also change. Adjusting coverage amounts accordingly helps you avoid paying for unnecessary protection and saves you money. Consider increasing deductibles, as this is a common way to lower premiums. Be sure to understand the impact that a higher deductible would have before choosing this option.
Open communication with your insurance agent is crucial. Regularly discuss your life changes and financial situation to ensure your coverage remains appropriate and cost-effective. They can help you find the optimal balance between adequate protection and affordable premiums.
Tips to Save Money on Insurance Premiums
Saving money on insurance premiums requires a strategic approach. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is crucial. Don’t settle for the first offer; shop around to find the best rates.
Increasing your deductible can significantly lower your premium. This means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim, but the trade-off is often worthwhile for lower monthly payments. Consider your risk tolerance carefully before making this decision.
Bundling your insurance policies, such as combining your auto and home insurance with the same company, often results in discounts. This is a simple way to save without sacrificing coverage.
Maintaining a good driving record and a safe driving history is paramount for auto insurance. Avoid accidents and traffic violations to keep your premiums low. Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving programs or telematics devices that track your driving habits.
Review your coverage annually. As your life changes, so should your insurance needs. Regularly reviewing your policy ensures you’re not paying for coverage you no longer require, saving you money in the long run.
Look for discounts offered by your insurer. Many companies provide discounts for things like home security systems, good grades (for students), or membership in certain organizations. Inquire about available discounts to potentially reduce your premiums.